New research from 主要研究 advances the understanding — and ultimately treatment — of a genetic mutation that causes vision disease and blindness.
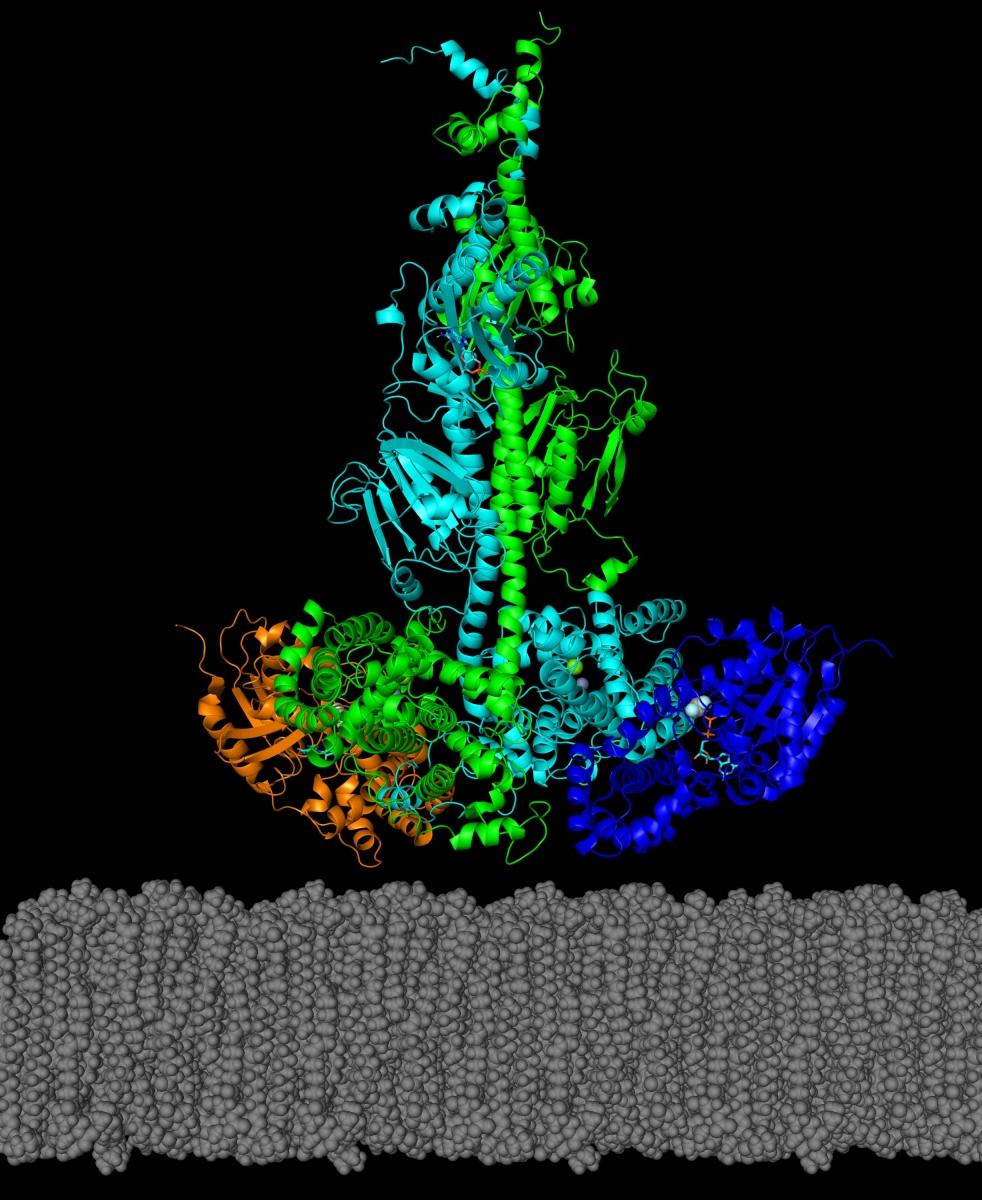
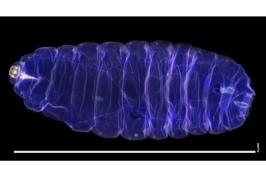
在最近发表于 生物化学杂志, 主要研究 researchers have reported the first structural model for a key enzyme, 它的激活蛋白, that can play a role in some genetically inherited eye diseases like retinitis pigmentosa and night blindness.
“There has been substantial research on the biochemical pathway involving this enzyme, 称为PDE6, but defining atomic-level models is important for locating PDE6 mutations in order to understand why they cause disease and how we can develop new therapeutic interventions to manage retinal diseases,” 里克古德他是 生物医学与生物工程综合研究中心 也是这项研究的首席研究员.
Vision starts in the photoreceptor cells of the retina which contains rods, 负责弱光视力, 和视锥细胞, 哪一个在明亮的光线下活跃并且有色觉. 当光被视杆细胞和视锥细胞吸收时, 它触发了激活磷酸二酯酶6的途径, 或PDE6. This generates a nerve impulse to the brain that ultimately results in visual perception. 一些遗传性眼病是由PDE6突变引起的, 或者它的激活蛋白, transducin, 这可能导致正常视力受损,甚至完全失明
"Defining atomic-level models is important for locating PDE6 mutations in order to understand why they cause disease and how we can develop new therapeutic interventions to manage retinal diseases.”
在研究中, the researchers reported how they were able to use chemical cross-linking combined with mass spectrometric analysis to resolve the structure of PDE6 in its nonactivated and transducin-activated states. This approach permitted visualization of flexible regions of individual PDE6 catalytic and inhibitory subunits that were poorly resolved in previous work as well as the overall molecular architecture of the activated protein complex.
“Determining the structure of these visual signaling proteins has always been a challenge because of their complexity,迈克尔·欧文说, 生物化学博士生,第一作者. “Having detailed structural information about how PDE6 is activated by transducin will help us understand the molecular causes of visual disorders and blinding diseases resulting from mutations in these proteins.”
Current medical treatment for such genetically inherited retina diseases may include gene therapy or drugs meant to inhibit the disease process. However, they are not always successful in restoring the balance of PDE6 and preventing blindness. Scientists believe that knowing the molecular structures of these visual signaling proteins and how they interact with each other can offer clues for the development of new drugs to both restore vision and prevent blindness.
这项研究是由国家眼科研究所资助的, 国家普通医学科学研究所, 国家儿童健康和人类发展研究所, 美国国家科学基金会和联合国大学研究办公室.
-
写的:
罗宾·雷,1982年 | 主要研究营销 | 罗宾.ray@femdomcenter.com | 603-862-4864