关键发现:
与水质区域的数字地图相结合的调查数据表明 支付意愿 for water quality improvements by households extends beyond their home area or iconic locations to areas that have individualized connections. 以前, it was believed that households place higher value on water quality improvements made 在ir own neighborhoods or in iconic areas such as vacation destinations.
支付意愿(WTP): 顾客愿意为产品或服务支付的最高价格.
It is traditionally assumed that the economic value of water quality improvements depends on where those improvements occur, with the belief that households will generally place higher value on water quality improvements made 在ir own neighborhoods or in iconic areas such as vacation destinations. 然而,主要研究 COLSA副教授 威尔弗雷德Wollheim collaborated on a recently released study that paired water quality scenarios with interactive maps, finding that households also value water quality improvements outside their local areas and/or in iconic locations. This finding suggests that historic policymaking around water quality improvements doesn’t accurately account for the entire scope of locations at which households would support water quality improvements.
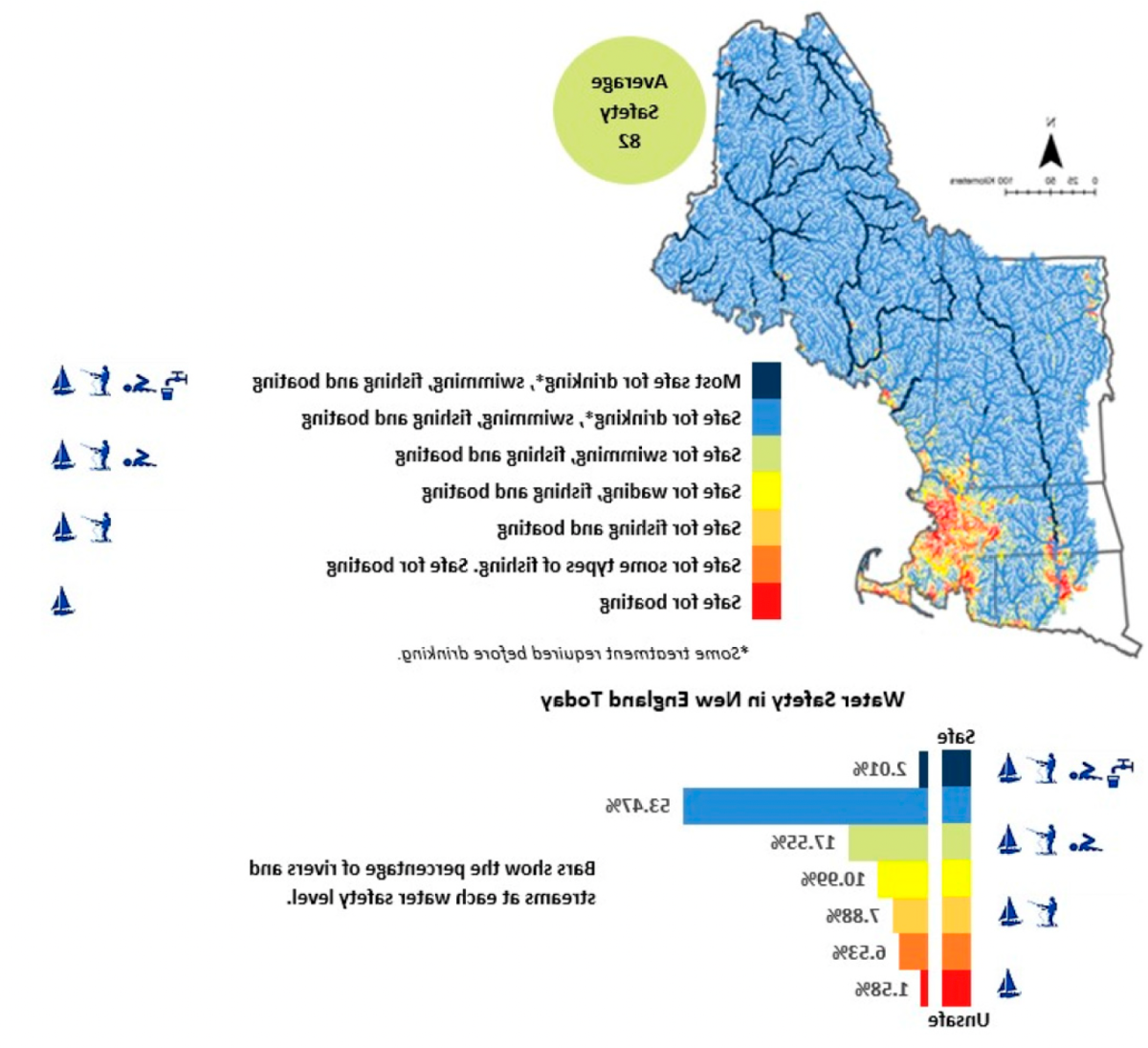
Wollheim,他也是 地球系统研究中心是该研究的共同作者之一 克拉克大学 同时也涉及到 弗吉尼亚理工大学 咨询公司 ICF国际. 他们的发现是 发表 在 美国国家科学院院刊. Wollheim提供了GIS地图,显示了95个网络的水质测量,800英里的河流和小溪将新英格兰地区的水抽干. The maps were based on models his team developed over the past two decades and showed different scenarios of water quality improvement that would result from better management of point and non-point pollution sources.
这些地图被用于在线调查, 分配给新英格兰六个州的家庭. 作为调查的一部分, 参与者可以在地图上缩放和平移,以查看现有的水质水平, 水质可能改善的不同情况, 以及改进的类型, 例如改善可用的饮用水和/或娱乐机会. Survey takers then answered a hypothetical referendum question asking whether they’d support the different scenarios — at an annual cost to their household — and why or why not.
“The interactive maps show where water quality is poor for different types of surface water use, 比如人类使用, 水生生物, 或者是水污染,沃尔海姆说, 主要研究的联合主任 水质分析小组 还有一位科学家 新罕布什尔州农业实验站. 在城市较多的地区,水质通常较差, 比如在波士顿和哈特福德附近, 还有新罕布什尔州南部, 他补充说.
“我们应用了合理的管理场景来创建地图, 展示了改进的范围和可能发生的地方, 调查对象被问及他们愿意为这些改进支付多少钱.沃尔海姆说. “It’s one of the first assessments of water quality value 在 nation that covers an entire region, 在新英格兰, 并且是基于现实的环境条件.”
共1个,698人参加了新英格兰水质改善调查, 和1,239名受访者使用了数字水图. The researchers found that when participants zoomed in to specific locations or panned across the maps, 三分之一的情况下,照片会包括这个人的家和, 意料之中的是, high values were placed on water quality improvements within 10-25 miles of their houses. The remainder of the time was spent investigating areas away from their homes — places that participants might vacation or recreate at or value for other reasons — and that they placed high values on water quality improvements to these areas as well.
“通过基于现实和区域水质预测的调查, the results will ultimately help us to more effectively manage water quality improvements and understand what factors that New England residents of all different geolocations (urban, suburban and rural) and socioeconomic levels consider when supporting freshwater management policies,Wollheim补充道.
这项研究得到了 U.S. 环境保护署STAR计划资助. 这本书是罗伯特·J. 庄士敦,Klaus Moeltner, Seth Peery, Tom Ndebele,姚振宇,Stefano Crema, Wilfred M. Wollheim和Elena Besedin.
你可以阅读发表的文章, 新英格兰河网水质价值的空间维度,在… 美国国家科学院学报(PNAS).
-
写的:
尼古拉斯·高斯林,06年 COLSA/NH农业试验站 尼古拉斯.gosling@femdomcenter.com