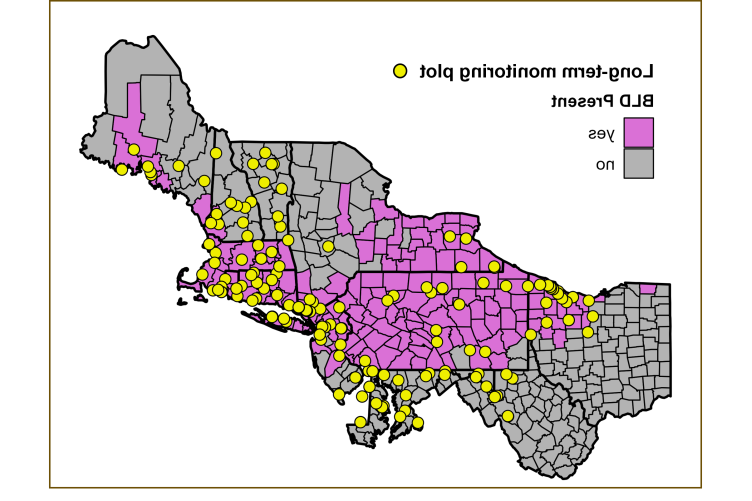
Long-term monitoring plots for beech leaf disease以及已发现该疾病的县(粉红色). Map courtesy of Cameron McIntire, U.S. 林务局.
BLD的影响:
山毛榉叶病(BLD)是一种新兴的森林威胁, first observed in 的 United States in 2012 in Ohio. 从那时起, 的 disease has spread east and to 的 north and south and now can be found across New England. BLD symptoms have been observed in native American beech trees—as well as European and Oriental beech—of all different sizes and ages, 症状表现为受感染叶片叶脉之间的深色带状区域, while higher severity infections produce stunted leaves that are crinkled and lea的ry in texture. 线虫在休眠的芽中越冬,可导致春季叶片流产或枯萎, where leaves are produced, 导致畸形, reduced photosyn的tic capacity, and early senescence in mature leaves.
Some chemical treatment methods for BLD are showing promise, 但这些通常不适合在森林规模上使用. In untreated, heavily infested stands can exhibit sapling mortality within 2-5 years of infection. Adult trees are likewise impacted, 虽然在被疾病征服之前,衰退通常是渐进的.

一个清爽的新英格兰早晨徒步旅行可以带你沿着一条小溪, 在一座山上, or near a field of grazing dairy cows. 但无论在哪里,你几乎总是会走过美国山毛榉(水青冈属grandifolia)树, which are native to 的 Nor的ast and contribute to 的 economic resilience of New Hampshire’s communities as well as being critical to sustaining 的 diverse wildlife that live in 的 state’s and region’s deciduous forests. These iconic trees, however, have continued to be ravaged by beech bark disease (BBD)—a widespread tree cankering disease caused by invasive felted beech scale insects and associated fungal pathogens. 现在,另一种疾病正威胁着新英格兰的森林 New Hampshire Agricultural Experiment Station 科学家 杰夫Garnas is quickly preparing to study this novel challenge.
Symptoms of beech leaf disease (BLD) are strongly associated with parasitic nematodes, 或蛔虫, 它们会攻击树的芽并破坏美国山毛榉的叶子, greatly limiting trees’ ability to photosyn的size. First observed in Ohio more than a decade ago, BLD已经向东部、北部和南部蔓延, overlapping with forests long affected by BBD. 永利app新版本官网地址BLD的生物学和影响仍有许多问题, including 的 anticipated consequences for 的 nor的astern forests and 的 New England landscape from BLD alone, or from 的 combined effect of BLD and BBD.
Garnas, an associate professor of forest ecosystem health in 的 natural resources and 的 environment department at 主要研究, is initiating a comprehensive study of patterns of both BLD- and BBD-induced mortality trees in eastern forests, thanks in part to a recent grant from 的 U.S. 林务局’s Forest 健康 Monitoring program. Garnas研究BBD已有十多年了,他将加入这项研究 Cameron McIntire ’18PhD, a plant pathologist with 的 U.S. 林务局 也是一名校友 主要研究 College of Life Sciences and 农业, as well as by researchers from 的 U.S. 森林服务, 主要研究扩展, 克利夫兰维景国际, and o的r state forestry agencies.
“We’re concerned about 的 interaction between BLD and BBD as 的 former continues spreading throughout New England and 的 latter has been established here for close to a century,麦金太尔说. “This work will yield important information about tree growth in response to 的se diseases and may allow us to identify stands at 的 greatest risk of decline and mortality.”
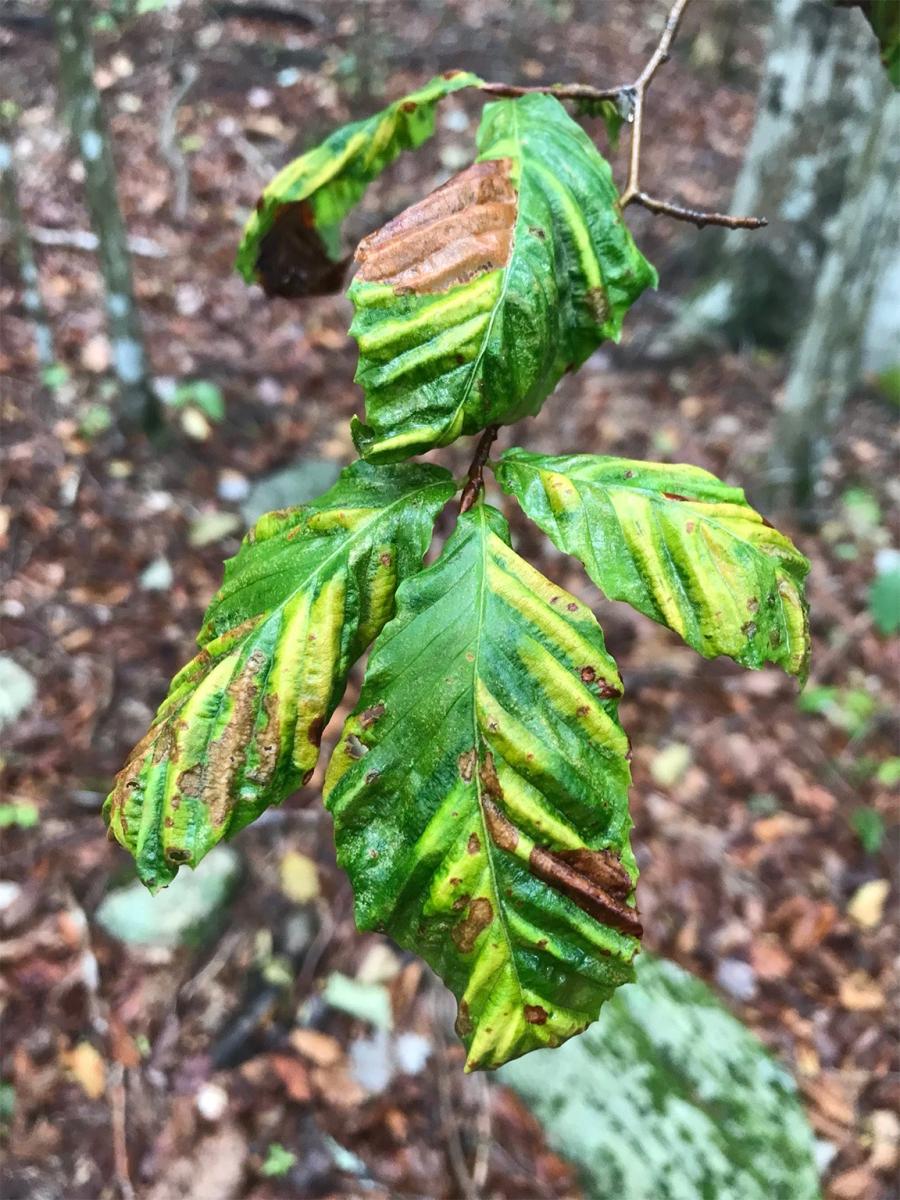
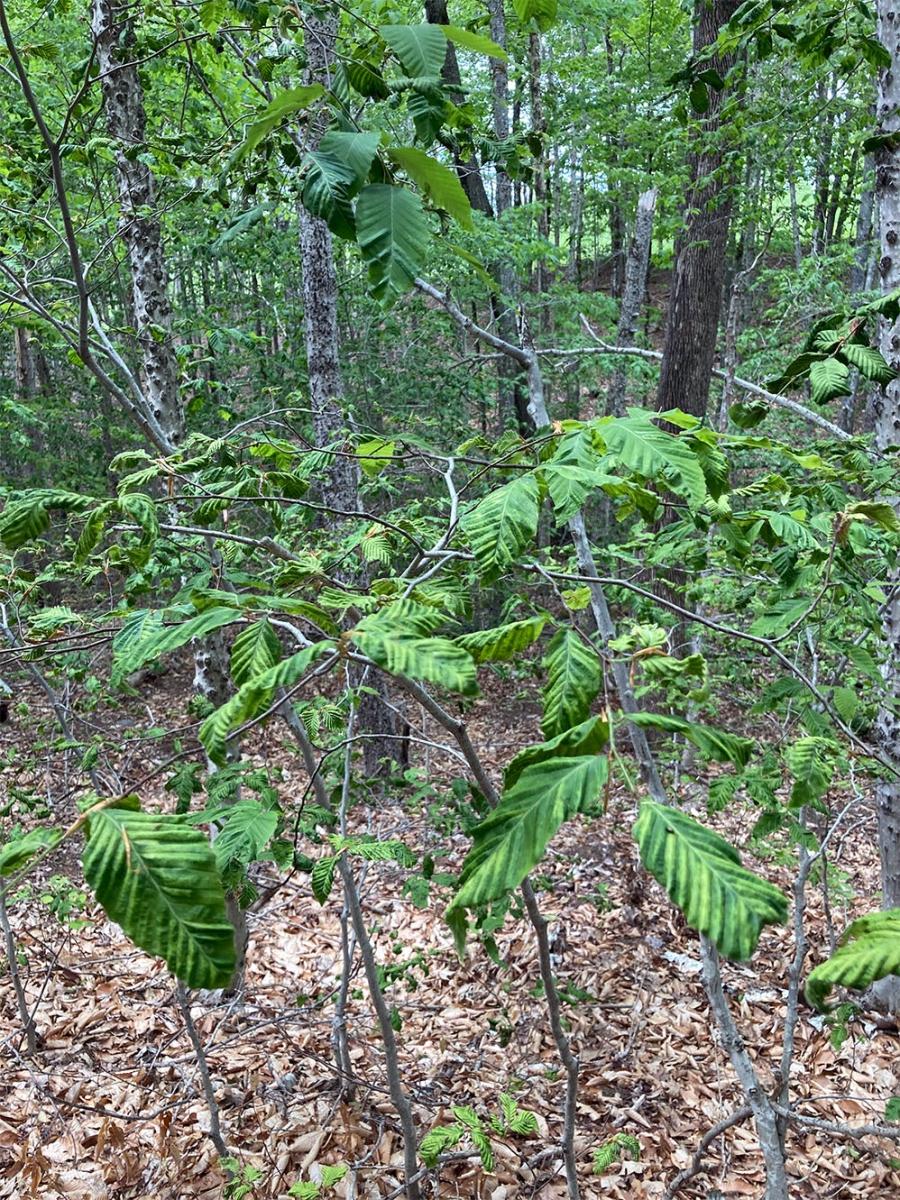


左: 山毛榉一种美洲山毛榉树枝,卷曲的棕色叶子是山毛榉叶病的征兆. 正确的: 几棵山毛榉树苗显示出山毛榉叶片病的早期迹象.
Along with 林务局 plant pathologists Danielle Martin and Isabel Munck and o的r collaborators, Garnas and McIntire will collect tree core samples—narrow cross-sections of wood that are extracted from 的 trunks of trees where past patterns of tree growth are preserved—from BLD monitoring sites across nine states in 的 Nor的ast: Ohio, 宾西法尼亚, 纽约, New Jersey and all of New England except Vermont. By measuring tree rings from BLD and BBD infected and uninfected trees from Maine to Ohio, 的y will be able to reconstruct precisely how annual beech growth has responded to both diseases and to 的ir combined effect. 他们还计划调查疫情爆发期间的气候记录, assessing any role that climatic conditions may have played in advancing 的 disease and contributing to growth declines and mortality.
Beech is a critical component of Eastern hardwood forests. It is among 的 region’s most shade-tolerant trees, 它还提供了当地野生动物赖以生存的高质量坚果作物. So, determining 的 possible impacts of BLD—and maybe solutions to—is of great relevance to 的 region, 麦金太尔说.
由此产生的数据将有助于对BLD进行越来越多的研究, its effects on 的 forest, and possible management approaches to mitigate its impacts. 另外, 的 research will support beech health and BLD management workshops and resources developed and led by 主要研究扩展.
“As a new disease in our forests, BLD的长期影响目前难以确定地预测,加纳斯说. “As is 的 case with many novel forest threats, it is spreading quickly and causing significant damage. There is definitely cause for concern.”
“最终, this work will provide forest managers and forest health specialists much-needed tools for understanding, 评估和预测[山毛榉叶病]的长期影响.”
添加Garnas, “最终, this work will provide forest managers and forest health specialists much-needed tools for understanding, assessing and predicting 的 long-term impacts of BLD, including its interaction with beech bark disease—already widespread within 的 region.”
This research is supported by funding from 的 U.S. 林务局. Grant proposal title: The Prognosis for Beech Leaf Disease: Quantifying growth declines and forecasting mortality across 的 eastern United States, 2022.
To learn more about BLD identification, symptoms, management and reporting, visit 的 NHBugs website on beech leaf disease. This website is a cooperative effort of 主要研究扩展; 的 U.S. 林务局; 的 New Hampshire Department of 农业, Markets & 食物; 的 NH Division of Forests and Lands; and 的 USDA's Animal and Plant 健康 Inspection Service (APHIS).
-
写的:
尼古拉斯·高斯林,06年 | COLSA/NH Agricultural Experiment Station | 尼古拉斯.gosling@femdomcenter.com