认识一下海洋生物学家格兰特·米尔恩
关键发现:
采用被动声监测和元条形码海水样本的组合, 研究人员 主要研究生命科学与农业学院 和 主要研究声学研究中心 & 教育 评估了缅因湾三个沿海海洋栖息地的生态连通性. The scientists found that the combined method offered a more wholistic picture of biological connectivity in terms of ecology and function.
关键术语:
生态(或生物)连通性: 展开定义
Refers to the movement of organisms among different habitats or areas that can influence population dynamics, 遗传多样性与生态系统功能.
功能连通性: 展开定义
Refers to the ecological processes that occur among different habitats or areas that can influence ecosystem productivity, 营养循环和生态系统功能的其他方面. 功能连通性可受到物理因素(如水流)的影响, as well as biological factors such as the movement of organisms that play important roles in ecosystem processes.
metagenomics: 展开定义
A field of study that uses DNA sequencing technology to identify and analyze the genetic material (e.g.(DNA)从混合的生物体(如.g.(细菌、真菌和病毒)在土壤、水或空气等环境样本中. This approach allows scientists to study the diversity and function of entire communities in their natural environments.
Metabarcoding: 展开定义
一种在metagenomics学中使用的针对特定DNA标记的方法.e., DNA sequences that are unique to a particular group of organisms) to identify the organisms present in a sample. 通过将从样本中获得的DNA序列与参考数据库进行比较, 科学家可以识别样品中存在的不同物种并估计它们的丰度.
元条形码海水样本(MSS): 展开定义
A technique used to identify the genetic material from different types of organisms present in a sample of seawater.
被动声监测(PAM): 展开定义
一种用于监测自然环境中声音的技术.g.(海洋、森林),而不干扰被研究的生物. This involves deploying underwater hydrophones or terrestrial microphones to capture sounds made by the environment (e.g.(如风、浪、冰雨)和生物(如海水).g.、鲸鱼、鸟类、昆虫). 分析录音中的信号可以让我们深入了解动物的行为、交流和生态.
时空尺度: 展开定义
用空间和时间来描述研究范围和持续时间的一种方法. 空间尺度是指研究的面积或范围.g., local, regional, global), whereas temporal scales refer to the duration or frequency of a study (e.g.(秒、分、时、日、年、年). Understanding spatiotemporal scales is important in ecology because it helps scientists determine the appropriate methods and tools to use for their study and interpret their results in a meaningful way.
音景生态: 展开定义
The study of acoustic relationships that exist among organisms (including humans) 和ir environments.
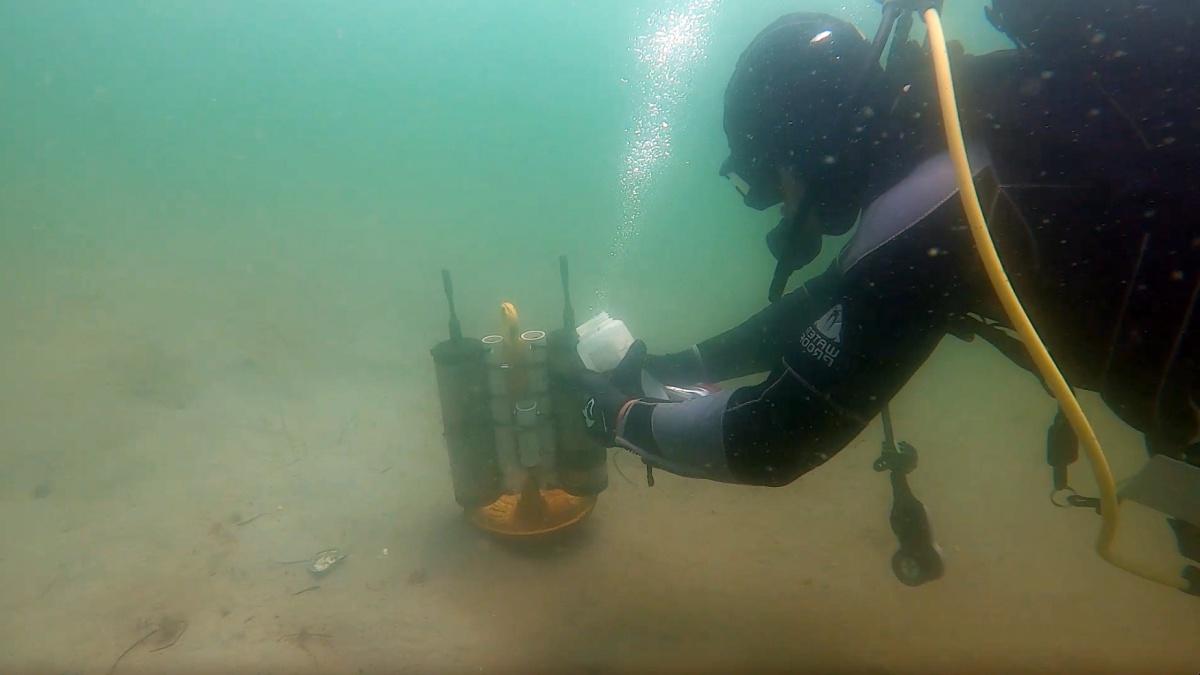
在过去的两个夏天,海洋生物学博士生 格兰特米尔恩 他每周都要在纽卡索海岸附近待几天.H.缅因州的福斯特堡收集声音和水样. 戴上潜水装备, 部署水听器(水下麦克风)和携带水采样容器, 米尔恩通过一种叫做 被动声监测, 或帕姆, in three habitat types to better underst和 connectivity of these potentially at-risk Gulf of Maine areas—as well as investigate how natural or human change would impact their soundscapes. 米尔恩的研究和类似的研究发生在 主要研究生命科学与农业学院 (COLSA)代表了一种新兴的, non-destructive approach to studying natural environments and conservation ecology—by comparing soundscapes and genetic makeup, 并跟踪他们一段时间, 评估人为影响和环境变化的其他原因.
“The ability to assess the acoustic environment through minimally invasive monitoring techniques is valuable for managing marine ecosystems, 特别是在人为噪音的影响方面,米尔恩描述道。. 此外,观察 生物和声学连通性 对于评估对周围栖息地声景的间接影响是有价值的, 特别是当一个栖息地的音景经历自然或人为引起的变化时.”
最近,米尔恩发表了他的研究结果 问题的研究 海洋学. 米尔恩是这篇论文的第一作者,他是 邦妮布朗生物科学系教授兼系主任 詹妮弗Miksis-Olds他是 主要研究声学研究与教育中心. 米尔恩一直在追求他的兴趣 metagenomics-对从环境中提取的样本中发现的遗传物质的研究 布朗大学的生态遗传学实验室.
“我的研究着眼于三种特殊的沿海海洋栖息地:普通鳗鱼草(目前)在由沙和泥构成的柔软海床中, 大型藻类群落位于由砾石床和巨石组成的坚硬海床上, 柔软的海底没有鳗鱼草,米尔恩说。. “我和我的同事每周都会去我们的采样点几次, 然后把我们的样本带回实验室进行分类和排序.”
在Miksis-Olds的声学研究实验室,Milne使用“音景的代码由合著者迪伦·威尔福德在《永利app新版本官网地址》中提出. The code helped compare the soundscapes of different habitats and geographic regions and allowed the scientists to determine whether there are significant relationships or differences among the soundscapes of the three habitats.
和格兰特米尔恩一起在缅因湾潜水
“Grant’s work is progressive in that the combination of acoustics and genomics provides more information about the environment together than either sensing method does alone,米克西斯-奥尔兹解释道. “PAM only provides information on animals or sources generating sound (silent animals or sources go undetected). 基因组信息, 有可能了解到在生态系统中存在但沉默的动物.”
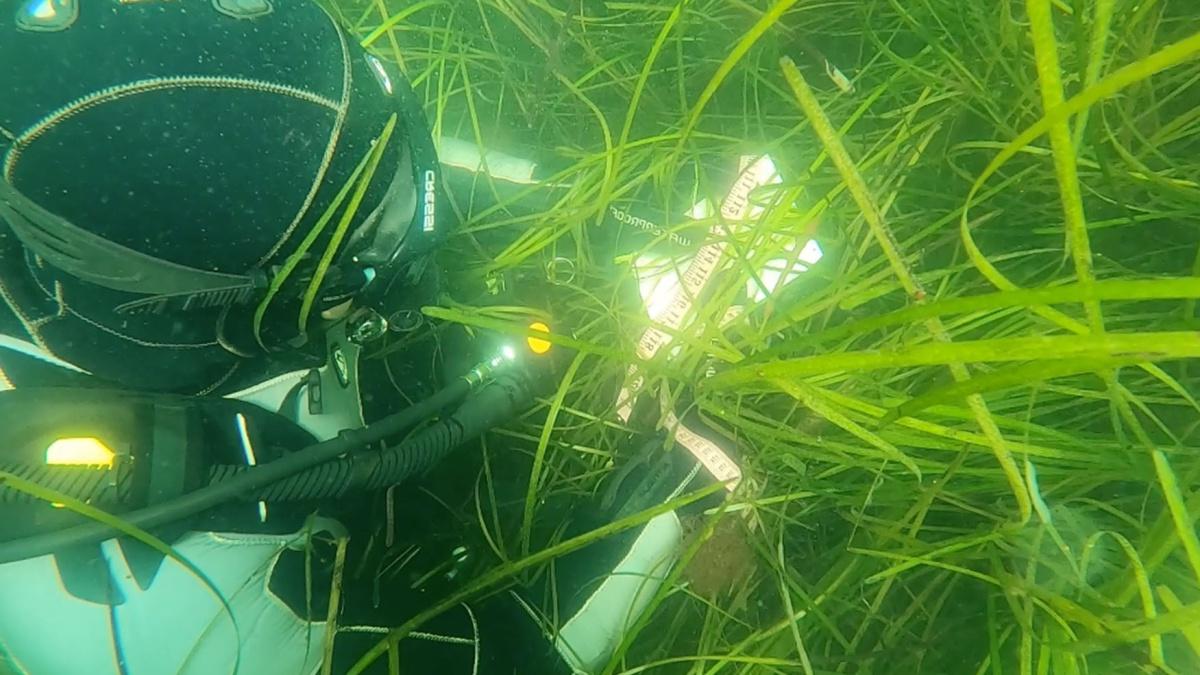


在布朗的生态遗传学实验室, Milne isolated organic matter found in the water samples and sequenced the DNA to determine which plants and animals were present. 为了做到这一点,他使用了一种叫做 对海水样本进行元条形码编码 (MSS), which amplifies 和n sequences the genetic material from various organisms found in a single sample of seawater and compares the DNA to a database to determine from which organisms the DNA was derived.
“Metagenomics allows us to detect living members of communities without actually capturing the species—instead using microbes, 短暂物种留下的粪便或脱落的细胞, 或者从陆地冲进水中的生物体的全部或部分, 例如,布朗说. “Grant’s work to combine MSS with PAM is pushing the envelope of non-destructive environmental sampling.”
“这个项目最初让我感兴趣的是涉及生态遗传学的工作, 我本科学的是什么,米尔恩补充道。. “然而, 在这项研究中, I also grew to appreciate the power of acoustics as a tool for monitoring and managing ecosystems and continue to realize the research opportunities in this field.”
This material is based on work supported by the 主要研究声学研究与教育中心 (CARE) through funding from the Office of Naval Research Award N00014-19-1-2515 to J. Miksis-Olds. Milne也得到了COLSA的资助. 这项研究是由格兰特米尔恩, 詹妮弗Miksis-Olds, Alyssa Stasse, Bo-Young李, 迪伦·威尔福德和邦妮·布朗.
你可以阅读发表的文章, Evaluating Connectivity of Coastal Marine Habitats in the Gulf of Maine by Integrating Passive Acoustics and Metabarcoding, in 海洋学.
-
写的:
尼古拉斯·高斯林,06年 COLSA/NH农业试验站 尼古拉斯.gosling@femdomcenter.com